

EnglisH AcademY
Online... ...
English language
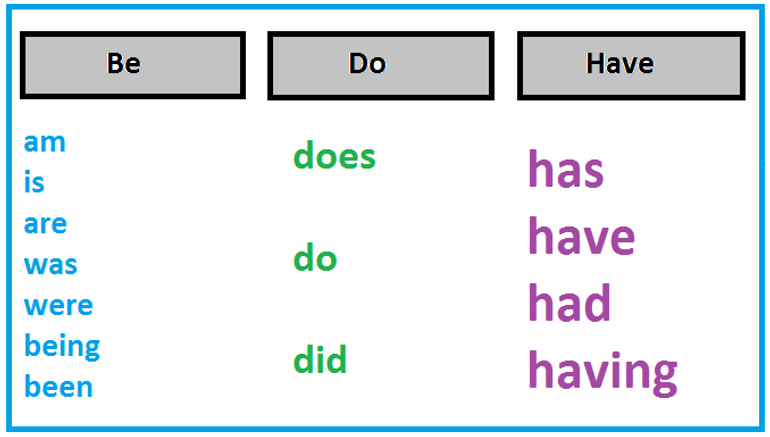
Auxiliary verbs
Auxiliary verbs are used together with a main verb to give grammatical information and therefore add extra meaning to a sentence.
To Be,to Do and to Have are auxiliary verbs, they can be used as main verbs.
Understand the dual nature
To be, to do, and to have are both stand-alone verbs and auxiliary verbs.
stand-alone verbs:
Freddy is nervous because of the exams.
auxiliary verbs:
Freddy is studying hard to pass the exams.
stand-alone verbs:
We did our homework
auxiliary verbs:
We did play after
stand-alone verbs:
Selena has twelve orange
auxiliary verbs:
Selena has bought a catfish
To be
Be is the most common verb in the English language. It can be used as an auxiliary and a main verb. It is used a lot in its other forms.
Base form = be
Present form = am/is/are
I am
You are
He is
She is
It is
We are
They are
You are
Progressive tenses with the auxiliary verb to be.
All progressive (continous) tenses use a form of be.
Present Participle / Gerund = being
Past perfect continuous with the auxiliary verb to be.
All past perfect continuous tenses use a form of be.
Past Participle = been
To do
The verb do is one of the most common verbs in English. It can be used as an auxiliary and a main verb. It is often used in questions!
Base form = do
Present form = do/does
I do
You do
He does
She does
It does
We do
They do
You do
Negative form with the auxiliary verb to do.
All negative forms of a verb use the auxiliary to do.
We use the verb to do deny actions, or to express the negative form of an action either in present simple or past simple, by simple adding "not" after the auxiliary "do".
Affirmative form Negative form
I like to jump I do not like to jum
I love shrimp I do not love shrimp
She loves She does not love
He walks He does not walk
NOTE: Verbs in third person add an "s" at the end of the verb e.g. To love- She loves.When we use does not, we do not add an "s" .
Present Simple= do/ does Present Simple (negative form)= don't/ doesn't
Past simple of any verb by simply adding "Did".
We use the auxiliary verb to do in past form to express verbs in past simple.
Infinitive form Present simple Past simple
To buy I buy I did buy = I bough
To swim You swim You did swim = You swam
To learn He learns He did learn = He learned
To call She calls She did call = She called
To walk We walk We did walk = We walked
To play They play They did play = Thay played
As you can see whenever you use "did" to say verbs in past simple, you do not say that verb in past
simple.
Now we do the same thing with "did" to deny things tha happened in the past.
We add not so it will be "did not" or the contraction "didn't"
Negative Negative Short Form
I did not walk I didn't walk
you did not play you didn't play
he did not cook he didn't cook
she did not listen she didn't listen
it did not rain it didn't rain
we did not eat we didn't eat
they did not drink they didn't drink
Past Simple = did
Questions with verbs in the simple present use the auxiliary verb “DO”.
Simple present Question in simple present
You play tennis on weekends Do you play tennis on weekends?
I act weird sometimes Do I act weird sometimes?
She has so much to give Does she have so much to give?
He sings in the shower Does he sing in the shower?
We like pizza Do we like pizza?
They live close to the airport Do they live close to the airport?
Now we do the same thing with "did" to ask things that happened in the past.
We simply change "do/does" for "did" at the begenning of the question and we finish with a question mark?
Present simple questions Past simple questions
Do I walk? Did I walk?
Do you play? Did you play?
Does he cook? Did he cook?
Does she listen? Did she listen?
Does it rain? Did it rain?
Do we eat? Did we eat?
Do they drink? Did they drink?
Past simple = did
Do is used to add emphasis to the main verb,
that is, to make the expression or feeling stronger.
Examples:
I believe in you I do believe in you
You love her You do love her
He studies hard He does study hard
or it could be also used in the past form
They arrived on time They did arrive on time
We finished the course We did finish the course
To have
Have is one of the most common verbs in the English language.
Base form = have
Present form = have / has
I have
You ave
He has
She has
It has
We have
They have
You have
Past perfect with the auxiliary verb to have
All perfect tenses use a form of have.
Present Simple = have/has
Past Simple = had




Past form = was/were
I was
You were
He was
She was
It was
We were
They was
You were
Past form = did
I did
You did
He did
She did
It did
We did
They did
You did

Past form = had
I had
You had
He had
She had
It had
We had
They had
You had
How to make questions with auxiliary verbs?
As auxiliaries, the verbs be, have and do can change form to indicate changes in subject and time.
-
He had won the election.
-
They did write that novel together.
-
I am going now.
-
He was winning the election.
-
They have been writing that novel for a long time.
-
I shall go now.
"Shall", "Will" and forms of have, do and be combine with main verbs to indicate time and voice.
In England, shall is used to express the simple future for first person I and we, as in
"Shall we meet by the river?"
Will would be used in the simple future for all other persons.
Using will in the first person would express determination on the part of the speaker, as in
"We will finish this project tonight!
Using shall in second and third persons would indicate some kind of promise about the subject, as in
"This shall be revealed to you in good time."
This usage is certainly acceptable in the U.S., although shall is used far less frequently.
The distinction between the two is often obscured by the contraction 'll, which is the same for both verbs.
In the United States, we seldom use shall for anything other than polite questions (suggesting an element of permission) in the first-person:
-
"Shall we go now?"
-
"Shall I call a doctor for you?"
In the U.S., to express the future tense, the verb will is used in all other cases.
Shall is often used in formal situations (legal or legalistic documents, minutes to meetings, etc.) to express obligation